Wolfram|Alpha can quickly and easily compute the present value of money, as well as the amount you would need to invest in order to achieve a desired financial goal in the future. Plots are automatically generated to help you visualize the effect that different interest rates, interest periods or future values could have on your result. And now that we know how to estimate the Present Value of multiple cash flows, we can think about what the Present Value formula actually looks like. The approach to discount these 3 cash flows is actually identical to the case of the single cash flow we saw earlier.
What are the primary capital budgeting techniques?
Present value (PV) is the current value of a future sum of money or stream of cash flows. It is determined by discounting the future value by the estimated rate of return that the money could earn if invested. Present value calculations can be useful in investing and in strategic planning for businesses. The discount rate is actually a proxy for risk, and therefore, it’s how we penalise future cash flows for their level of risk. Conceptually, any future cash flow expected to be received on a later date must be discounted to the present using an appropriate rate that reflects the expected rate of return (and risk profile). Using the concept of present value, investors are able to project future cash inflows from an investment and convert these into their present value or today’s dollars.
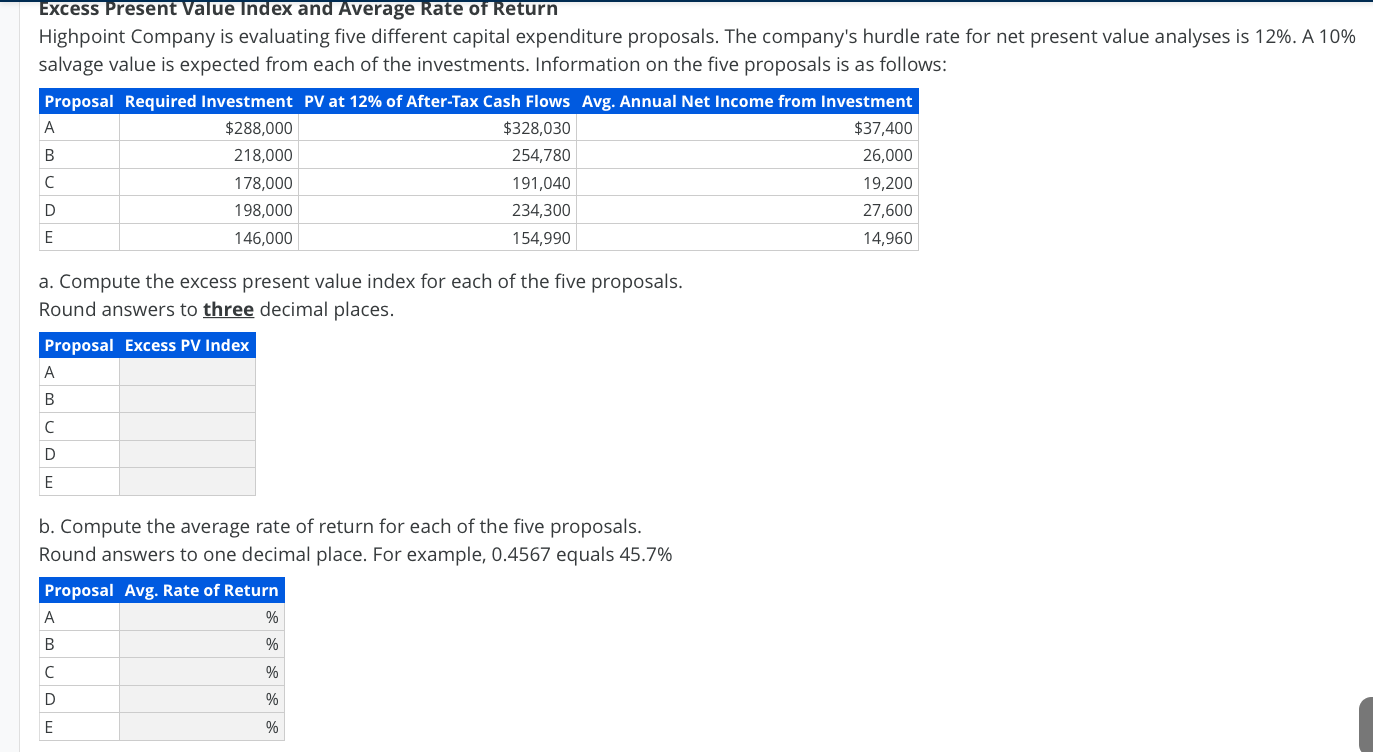
Profitability Index
The reduction in cost is considered equivalent to increase in revenues and should, therefore, be treated as cash inflow in capital budgeting computations. The sum of all the discounted FCFs amounts to $4,800, which is how much this five-year stream of cash flows is worth today. The present value (PV) formula discounts the future value (FV) of a cash flow received in the future to the estimated amount it would be worth today given its specific risk profile.
Subtract Initial Investment From Sum of Present Values
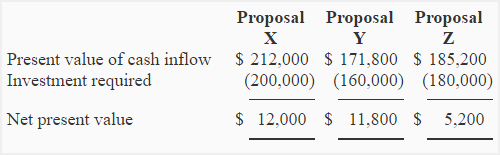
Shorter payback periods are generally more attractive, as they indicate faster recovery of the initial investment. Comparing NPVs of projects with different lifespans can be problematic, as it may not adequately account for the difference in the duration of benefits generated by each project. At the beginning of 2024, a business enterprise is trying to decide between two potential investments.
Interpretation of Net Present Value Results
Given a higher discount rate, the implied present value will be lower (and vice versa). This is because a higher interest rate diminishes the worth of future money today. For information pertaining to the registration status of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing. By utilizing these financial tools effectively, investors and financial managers can optimize their investment portfolios and maximize their returns on investment. Both PV and NPV are important financial tools that help investors and financial managers make informed decisions. Understanding PV is essential for making informed decisions about the allocation of resources and the evaluation of investment opportunities.
- Additionally, you can put this sum to work through an investment or risk-free saving account and earn interest on it, growing the amount you initially had.
- Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications.
- Shorter payback periods are generally more attractive, as they indicate faster recovery of the initial investment.
- When you are evaluating an investment and need to determine the present value (PV), utilize the process described above in Excel.
Market instability and fluctuations form an inherent part of business operations and can affect cash flows, inflation rates, and discount rates. Thus, depending on the current market conditions and future predictions, the present value needs to be reassessed periodically. PV is used to evaluate and compare different investment opportunities by calculating the present value of their expected future cash flows.
In essence, present value is a universal tool that aids financial analysts and investors in evaluating and comparing different investment opportunities. By discounting future cash flows back to their current worth, it allows them to make apples-to-apples comparisons and make informed decisions that potentially enhance wealth and ensure long-term financial success. It is a fundamental concept in finance that underpins many financial decisions, from simple investments to complex capital gain corporate finance strategies. Present value is the concept in finance that determines the current worth of a future sum of money or stream of cash flows given a specified rate of return. It contrasts future cash flows with their value today, factoring in the time value of money – the idea that money available now is worth more than the same amount in the future. The basic principle of bond pricing is that the price of a bond is the present value of its future cash flows.
It is essentially the interest rate used to depreciate future income, and its accurate estimation is paramount. However, determining an appropriate discount rate is challenging due to the numerous factors involved – risk-free rate, inflation expectations, risk premium, and more. By evaluating the present value of the expected future benefits, companies can gain a clearer understanding of the financial trade-off involved. If the expected future benefits, appropriately discounted to their present value, outweigh the project’s immediate costs, the companies might be willing to take the plunge and invest now. Each investment opportunity has a relative worth, and the principle of present value helps to quantify that worth today. It brings clarity to an investment’s potential gains or losses, allowing investors to make informed decisions.







